
The Ascent, a Motley Fool service, does not cover all offers on the market. As you can see in this example, the inventory purchased affects both the debit and the credit columns. For a step-by-step introduction, see our (relatively painless) guide to double-entry accounting. The example shows the electricity expense account which is on page 21 of the ledger. The name of the account ‘Electricity Expense’ and its account code 640 are also shown in the heading. A tool for federal agencies to send USSGL accounting issues to the USSGL staff.
- As outlined above, this means implementing regular account reconciliations and more frequent reviews of the general ledger.
- Now, each of your transactions follows a procedure before they are represented in the final books of accounts.
- Sometimes referred to as a book of original entry, the general journal lists all financial transactions of a business, and the general ledger organizes and balances transactions.
- In addition to the accounting ledger, there are several kinds of ledgers that you might use in the course of bookkeeping for your business.
- Posting transactions to your general ledger is part of the accounting cycle.
Bookkeeping Outline
To compare beginning and ending account balances, look at your company’s adjusted trial balance from the previous accounting period and the general ledger from this accounting period. For asset, liability, and equity accounts, match the ending balance on the trial balance to the general ledger’s beginning balance. Preparing a trial balance means adding debits and credits to ensure both columns match. This practice ensures your books are accurate and have no mathematical errors. Most companies prepare a trial balance at the end of each reporting period. A company’s total assets must equal the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity in a double-entry system.
- With its focus on reporting what happened (past transactions), some of the information in a general ledger might already be out of date, or it might not sufficiently reflect significant recent developments.
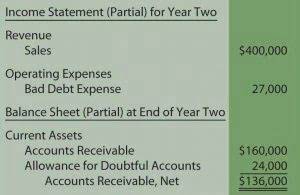
- The four remaining classifications of accounts are referred to as income statement accounts since the amounts in these accounts will be reported on the financial statement known as the income statement.
- Most importantly, from an accounting perspective, the general ledger includes debits and credits for each transaction.
- While this is easy to do for each individual vendor, using your general ledger to view all related expenses in each expense category provides you with a more encompassing view of your business expenses.
- This mitigates the risks that Centralized General Ledgers have from having one source control the ledger.
- If the assets you have recorded don’t equal the value of your equity plus liabilities, your account balances don’t match and need to be corrected.
List of General Ledger Accounts and Content
Even when using codes, your records should still include a description of each transaction. Then, even if you pass your books on to an accountant or bookkeeper, the descriptions will help them track what’s what. These codes are sometimes called an “account number.” In this example, all puppet-making-material purchases are coded 205, all sales revenue is coded 103, and so on. If you’re ever unsure what a certain code means, you can check back to your chart of accounts. Any accounts not in these ledgers such as asset, liability, and capital accounts remain in the general ledger. As with the main ledger, postings to the subledgers are from the books prime entry.
It’s how you get financial statements
In other words, these are the assets remaining after you pay off all the debts and the liabilities. In other words, you get a clear view of your business’s capacity to generate profits and the resources you have to meet outsider’s claims. This is because you can easily verify if various accounting general ledger account items are classified and recorded accurately with the help of the given information. You may choose to conduct an internal audit or get your accounts audited by an accounting professional. Therefore, General Ledger acts as an important financial record that is audited whatever may be the case.
Create correcting entries

One way to avoid errors is to use a POS system like Lightspeed Retail, which connects with accounting software to automatically sync data. To learn more about what Lightspeed Retail can do for your business, talk to an expert today. GnuCash includes excellent reporting options, with detailed asset and liability reports as well as a complete general ledger report.
What is a General Ledger (GL)? – TechTarget
What is a General Ledger (GL)?.
Posted: Mon, 07 Feb 2022 23:03:16 GMT [source]
Reconciling the general ledger ensures you correctly recorded each transaction by comparing source documents — statements, checks, and invoices — with accounting records. The general ledger is a fundamental tool in accounting that plays a crucial role in organizing and categorizing financial transactions. It serves as a comprehensive record of a company’s financial activities, providing a detailed account of all transactions. By utilizing sub-ledgers, businesses can streamline their financial management processes and gain a deeper understanding of specific areas of their operations. It enables them to have a more detailed analysis of their accounts, identify any discrepancies, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
- But since bookkeeping by hand takes 1,000 times longer, most business owners and bookkeepers use accounting software to build their general ledgers.
- Unlike Operating Expenses, the Non-Operating Incomes and Expenses are one-time incomes or expenses that you earn or incur.
- These financial statements include the income statement and balance sheet.
- The trial balance is checked for errors and adjusted by posting additional necessary entries, and then the adjusted trial balance is used to generate the financial statements.
- For example, the outstanding payments against suppliers, payments to be collected from customers, etc.
- These accounts help you in organizing the General Ledger Accounts properly and recording transactions quickly.

